There are nineteen types of objects available. They share a common set of properties but each also has its own specific properties; click the link for each one to see the specific properties.
Label: this is the most common object: it displays text, such as the contents of a field in the report's result set.
Check Box: this displays a Boolean (true or false or yes or no) field as a checked (for true) or unchecked (for false) check box.
Rich Text: some fields contain formatted text, such as red, bold, different fonts, and so on. These fields contain either Rich Text Format (RTF) or HyperText Markup Language (HTML), which uses codes to format the text. Displaying such a field using a Label displays the codes which is very difficult to read. Instead, use a Rich Text object, which displays the field's content with full formatting.
Picture Box: some fields contain either images or the path to an image file on disk. Use a Picture Box object to display such field or if you want to add an image such as a logo to the report.
Panel: a panel is used to contain other objects. This is often used to give those objects a common background color, such as these column headings enclosed within a panel with a dark grey background:
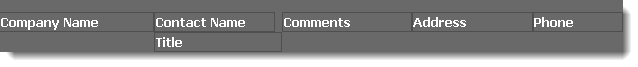
There are no specific properties for Panels.
Table: a table displays data in a spreadsheet-like format. Tables aren't used much in Report Writer except in cross-tab reports.
Line: draws a line on the report.
Shape: draws a shape on the report, such as a rectangle, ellipse, arrow, bracket, and so on.
Bar Code: displays the data for a field as one of several types of bar codes.
Zip Code: displays the data for a field graphically as a U.S. zip code.
Chart: charts the data as a pie chart, line graph, column chart, and so on. Adding a Chart to a report in the Advanced Report Designer doesn't work well because the result set likely isn't set up for it.
Gauge: charts the data as a linear or circular gauge.
Sparkline: displays a very small line chart, showing the general shape of the variation in some value.
Pivot Grid: this object is similar to a PivotTable in Microsoft Excel, showing data with variables in the rows and columns. Report Writer doesn't use this for cross-tab reports because they don't paginate very well. Adding a Pivot Grid to a report in the Advanced Report Designer doesn't work well because the result set likely isn't set up for it. Instead, create a cross-tab report.
Subreport: this includes another report within the report. Subreports are how Report Writer displays linked reports as drilldowns or embedded reports. Adding a Subreport to a report in the Advanced Report Designer doesn't work well because there isn't another report object available. Instead, using the subreport feature to add a subreport to the report.
Table of Contents: displays a table of contents for the report. A Table of Contents object can only be added to the ReportHeader or ReportFooter bands.
Page Info: this object is used to show the current date, page number, page count, or "Page X of Y" on a report.
Page Break: used to force a page break. Putting a Page Break in a group header band causes a page break when the group changes. Adding one to the detail band makes every record appear on its own page. There are no specific properties for Page Break objects.
Cross-band Line: like a Line, but this object can span multiple bands.
Cross-band Box: like Cross-band Line, this object can span multiple bands.
See the Layout Area topic for information on adding, moving, and resizing objects.
© IQ reseller, 1996-2020 • Updated: 04/17/18
Comment or report problem with topic
 Objects
Objects